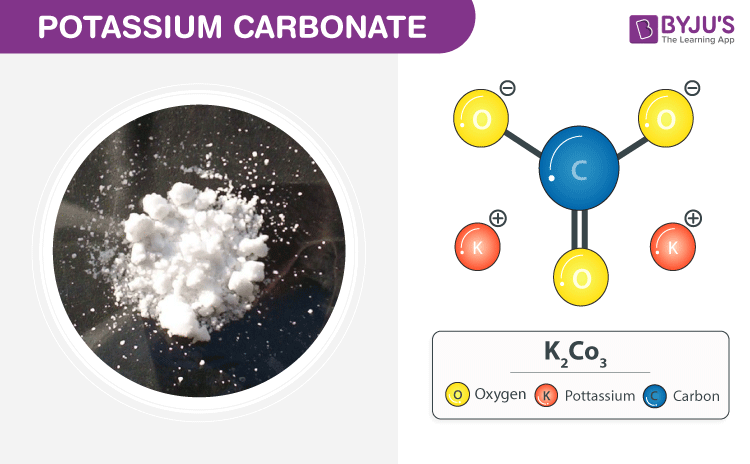
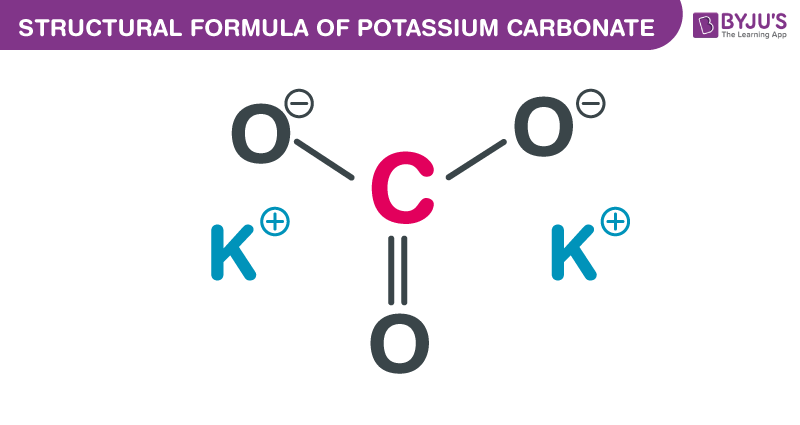
Potassium carbonate, also known as potash, is the commonly used base in chemistry. It is white, granular and translucent that tends to absorb water from the air. Potash is easily produced by pouring water over the ash of the burned plants kept in a large pot and then evaporating the solution formed. In this short piece of article, we shall be discussing the chemical and structural formula of potassium carbonate along with its few properties.
Properties of Potassium Carbonate
| Potassium Carbonate | |
| Name | Potassium Carbonate |
| Common Names | Potash, Pearl ash, salt of tartar, salt of wormwood |
| Appearance | White Hygroscopic Solid |
| Chemical Formula | K2CO3 |
| Melting Point | 891 °C |
| Boiling Point | Decomposes |
| Molecular Weight | 138.205 g/mol |
Potassium Carbonate Uses
- Used in the manufacture of fertilizers, heat resistant glass, soaps and chemical compounds
- Used in the manufacture of ink and pigments
- Used as a bleaching agent in the textile industry
- Used in pottery industry for glazing pots
- Used as a flux in the metal industry
To learn more about such chemistry topics register to BYJU’S now!
Comments